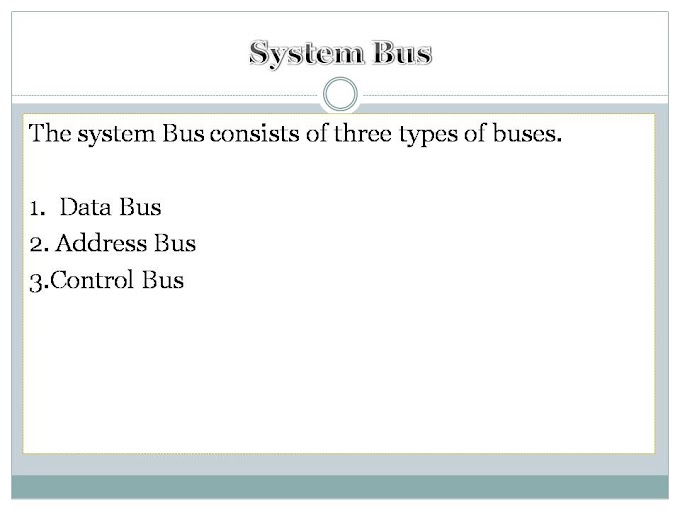
Basic Components of CPU
CPU Consists of the following basic Components.
1. Arithmetic and logic Unit (ALU)
2. Control Unit (CU)
3 Register
4. Cache
5. Internal Buses
Arithmetic and Logic Unit(ALU)
Arithmetic logic unit is the main processing unit of CPU. It performs arithmetic and logic operation on data. Arithmetic means addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and logical operation is the comparison between two data items. Arithmetic and logic Unit processes the data and then give back the results. The Result of an operation Are stored in register (temporary storage location). Now a day’s Central Processing units (CPU) have more than one Arithmetic and logic Units that can do the calculation simultaneously in order to improve the efficiency of computer system.

Control Units (CU)
Control unit manages the functions performed by different parts of the computer. It Coordinates and controls and the overall computer system, just like the brain controls the human body. It executes instruction, controls and directs the input, informs ALU (Arithmetic and logic Unit) for processing, arranges the storage and directs the data to the output device.
Control unit is responsible for directing the flow of instruction and data within control signals. The control signals. The control unit contains the necessary logic to interpret instructions and to generate the signals necessary for the execution of those instructions. The descriptive words “fetch” and “execute” are used to describe and a read control to unit. It fetches an instruction at by sending an address and a read command to the memory unit. The instruction at that memory address is transferred to the control unit for decoding. It then generates the necessary signals to execute the instruction.
Registers
Registers are small memory devices available in the CPU. These are used to store data temporarily. CPU register are at top of the memory hierarchy, and provides the fastest way for a cpu to access data. Each register is designed for a special purpose and the size of each varies. Register are measured ny the number of bits they can hold, like 8-bitsm 16 bits or a 32 –bits register. Processor contains different kinds of register and is classified according to their content or instruction.
CPU register are divided into two main types
General purpose register
Special purpose register
Cache Memory
It is the small amount of memory located between main memory and processor. Cache memory is also known as high speed buffer or a chip memory. The microprocessor stores a copy of most frequently used data and instructions in the cache memory. The microprocessors when desires and data its first look and to the cache memory, if not found their then it will ask for the same from the main memory. This will result in the better efficiency of the microprocessor speed and its usage.
There are different levels of cache memory
Level 1(L1) Cache memory resides inside the microprocessor and is very fast from the other memories Microprocessor first checks the level 1 cache memory.
Level 2 (L2) cache memory lies just outside the microprocessor, it is slow as instruction not found in level 1 cache memory the microprocessor will look in to level 2 cache memory.
Internal Buses
Bus
Data travels, inside the system through a communication path. These path are drawn on motherboard and joined different components of computer inside system.
Or
Bus is a data communication pathway through which data travels from are components to other, inside system.
Buses are used to carry data between CPU (central processing unit) and memory
Bus can be
Serial Bus
Parallel bus
Serial Bus
A type of bus that carries data through a single channel, is serial bus. In serial bus bit follows each other on single on a single channel.
Parallel Bus
A type of bus that carries data (bits) through multiple channel





0 Mga Komento